 Postdoctoral Researcher at Texas A&M University
Postdoctoral Researcher at Texas A&M UniversityJunwei currently holds a joint appointment as a Postdoctoral Researcher at Texas A&M University and a Research Scientist at Resilitix Intelligence LLC. He received his Ph.D. in Civil Engineering from Texas A&M University in 2025.
Junwei's research centers around four interconnected themes: Urban Resilience, Urban Systems, Urban Intelligence, and Urban Crises (4U).
Junwei's overarching research objective is to create new knowledge and methods in integrated intelligence to deliver transformative solutions that enhance resiliency, accessibility, inclusivity, sustainability, and equity (RAISE) in urban environments under ever-changing climate conditions.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Texas A&M UniversityPh.D. in Civil EngineeringSep. 2021 - Aug. 2025
Texas A&M UniversityPh.D. in Civil EngineeringSep. 2021 - Aug. 2025 -
 Southeast UniversityM.S. in Management Science and EngineeringSep. 2018 - Jun. 2021
Southeast UniversityM.S. in Management Science and EngineeringSep. 2018 - Jun. 2021 -
 Southeast UniversityB.E. in Construction ManagementSep. 2014 - Jun. 2018
Southeast UniversityB.E. in Construction ManagementSep. 2014 - Jun. 2018
Experience
-
 Urban Resilience.AI LabPostdoctoral ResearcherSep. 2025 - Present
Urban Resilience.AI LabPostdoctoral ResearcherSep. 2025 - Present -
 Resilitix Intelligence LLCResearch ScientistOct. 2025 - Present
Resilitix Intelligence LLCResearch ScientistOct. 2025 - Present -
 Texas A&M UniversityGraduate Research/Teaching AssistantSep. 2021 - Aug. 2025
Texas A&M UniversityGraduate Research/Teaching AssistantSep. 2021 - Aug. 2025
News
Selected Publications (View all )
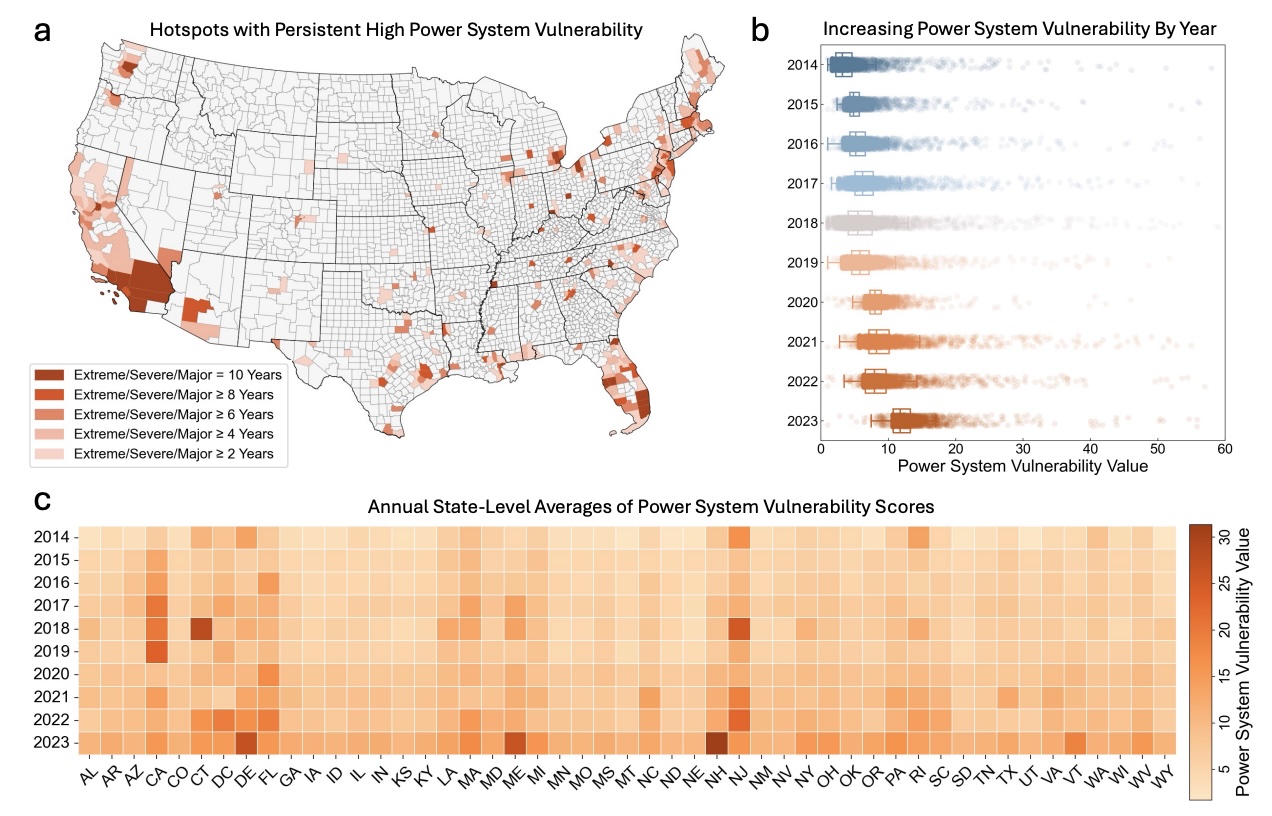
Establishing Nationwide Power System Vulnerability Index across US Counties Using Interpretable Machine Learning
Junwei Ma, Bo Li, Olufemi A. Omitaomu, Ali Mostafavi
Applied Energy 2025
We collected ~179 million power outage records at 15-minute intervals across 3022 US contiguous counties (96.15% of the area) from 2014 to 2023. We developed a power system vulnerability assessment framework based on three dimensions (intensity, frequency, and duration) and applied interpretable machine learning models (XGBoost and SHAP) to compute Power System Vulnerability Index (PSVI) at the county level.
Establishing Nationwide Power System Vulnerability Index across US Counties Using Interpretable Machine Learning
Junwei Ma, Bo Li, Olufemi A. Omitaomu, Ali Mostafavi
Applied Energy 2025
We collected ~179 million power outage records at 15-minute intervals across 3022 US contiguous counties (96.15% of the area) from 2014 to 2023. We developed a power system vulnerability assessment framework based on three dimensions (intensity, frequency, and duration) and applied interpretable machine learning models (XGBoost and SHAP) to compute Power System Vulnerability Index (PSVI) at the county level.
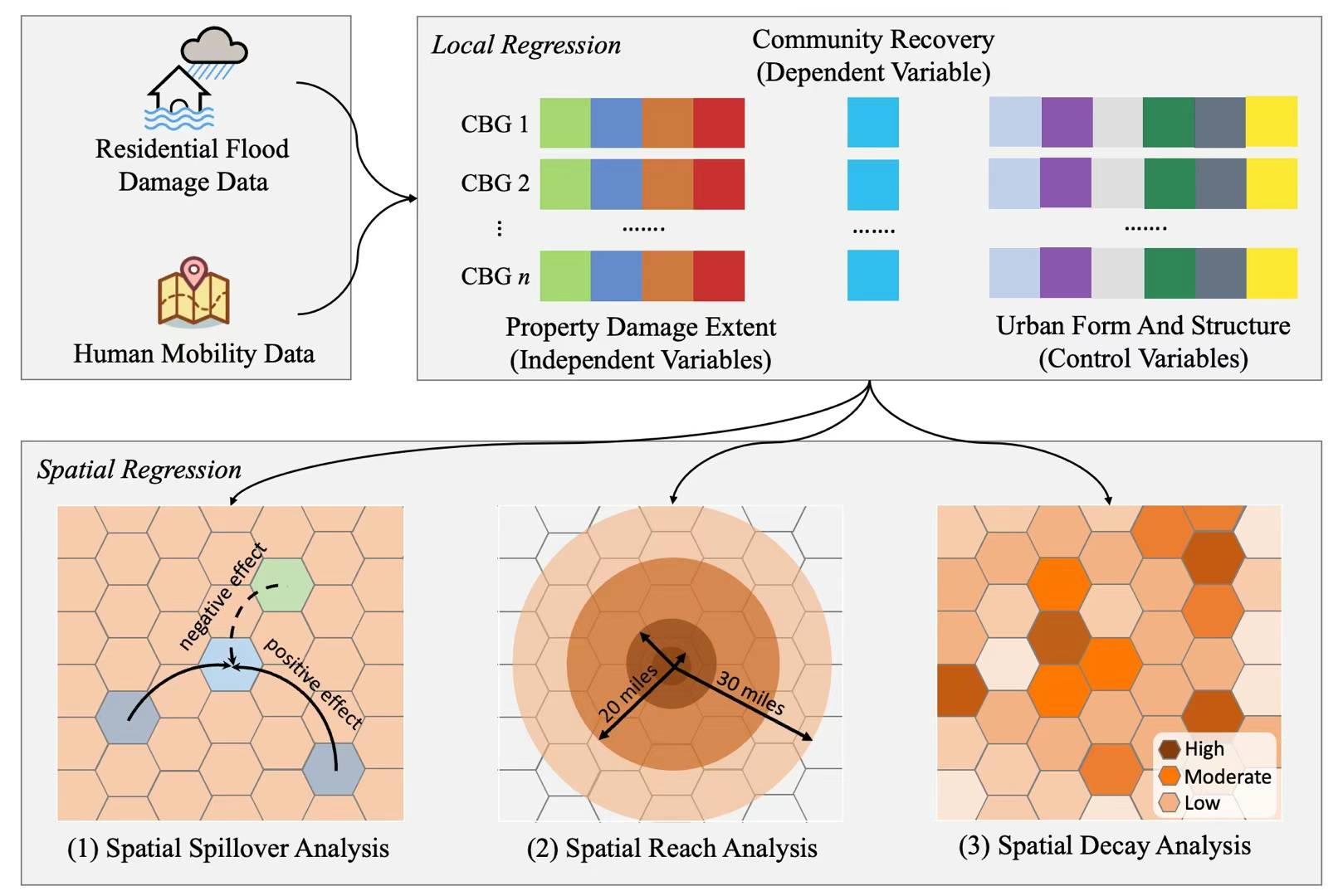
Non-locality and Spillover Effects of Residential Flood Damage on Community Recovery: Insights from High-resolution Flood Claim and Mobility Data
Junwei Ma, Russell Blessing, Samuel Brody, Ali Mostafavi
Sustainable Cities and Society 2024
We combined fine-resolution flood damage claims data (composed of both insured and uninsured losses) and human mobility data (composed of millions of movement trajectories) during the 2017 Hurricane Harvey in Harris County, Texas, to specify the extent to which vulnerability of the built environment (i.e., flood property damage) affects community recovery (based on the speed of human mobility recovery) locally and regionally.
Non-locality and Spillover Effects of Residential Flood Damage on Community Recovery: Insights from High-resolution Flood Claim and Mobility Data
Junwei Ma, Russell Blessing, Samuel Brody, Ali Mostafavi
Sustainable Cities and Society 2024
We combined fine-resolution flood damage claims data (composed of both insured and uninsured losses) and human mobility data (composed of millions of movement trajectories) during the 2017 Hurricane Harvey in Harris County, Texas, to specify the extent to which vulnerability of the built environment (i.e., flood property damage) affects community recovery (based on the speed of human mobility recovery) locally and regionally.
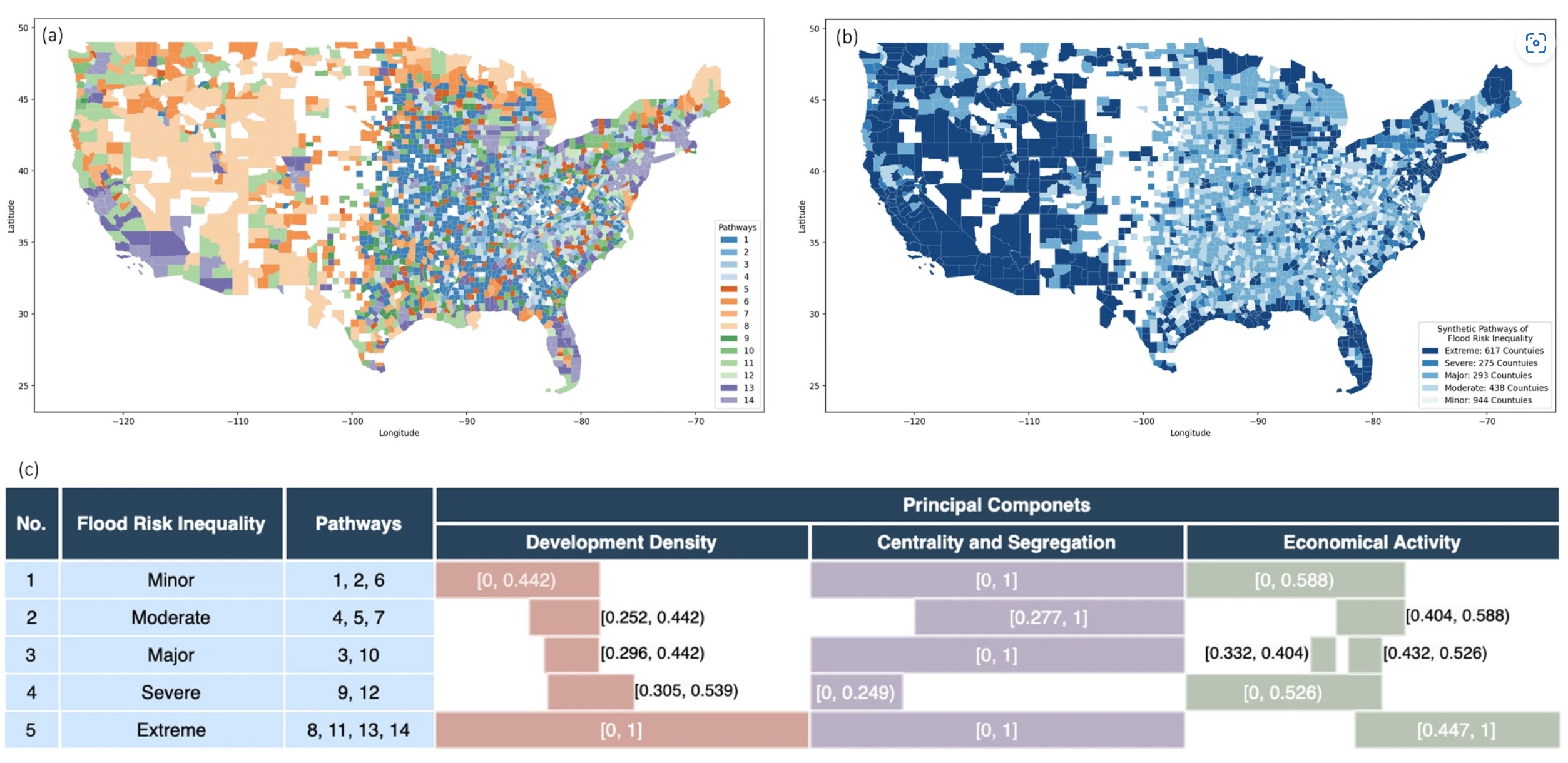
Urban Form and Structure Explain Variability in Spatial Inequality of Property Flood Risk among US Counties
Junwei Ma, Ali Mostafavi
Communications Earth & Environment 2024
We begin by evaluating spatial inequality of property flood risk using the metric of spatial Gini index (SGI), a measure of spatial inequality, for 2567 counties in the United States, identifying notable variations in spatial inequality of property flood risk across counties. We then explore how urban form and structure may be shaping this spatial inequality of property flood risk, by examining eight distinct urban features to assess their potential relationships.
Urban Form and Structure Explain Variability in Spatial Inequality of Property Flood Risk among US Counties
Junwei Ma, Ali Mostafavi
Communications Earth & Environment 2024
We begin by evaluating spatial inequality of property flood risk using the metric of spatial Gini index (SGI), a measure of spatial inequality, for 2567 counties in the United States, identifying notable variations in spatial inequality of property flood risk across counties. We then explore how urban form and structure may be shaping this spatial inequality of property flood risk, by examining eight distinct urban features to assess their potential relationships.